Messerschmitt Me 210 Video - Historical overview
|
|

Picture - A Luftwaffe Me 210 A-1 of the Versuchsstaffel 210 test squadron, over France in 1942
Role: Heavy fighter, Ground-attack aircraft Fighter-bomber, Bomber destroyer, Dive bomber
Manufacturer: Messerschmitt, Dunai Repx¼lÅ‘gépgyx¡r Rt.
First flight: September 1939
Introduced: 1943
Retired: 1945
Primary users: Luftwaffe
Hungary
Number built: 90 finished and 320 partially completed in Germany, 272 in Hungary
Developed from: Bf 110
Variants: Me 410
The Messerschmitt Me 210 was a German heavy fighter and ground-attack aircraft of World War II. The Me 210 was designed to replace the Bf 110 in heavy fighter role, design started before the opening of World War II. The first examples of the Me 210 were ready in 1939, but they proved to have poor flight characteristics. A large-scale operational testing programme throughout 1941 and early 1942 did not cure the aircraft's problems. The design eventually entered limited service in 1943, but was almost immediately replaced by its successor, the Messerschmitt Me 410 Hornisse ("Hornet"). The Me 410 was a further development of the Me 210, renamed so as to avoid the 210's notoriety. The failure of the Me 210's development programme meant that the Luftwaffe was forced to continue fielding the outdated Bf 110, to mounting losses.
Design and development
Messerschmitt designers had started working on an upgrade of the Bf 110 in 1937, before the production version of the Bf 110 had even flown. In late 1938, the Bf 110 was just entering service, and the RLM started looking ahead for its eventual replacement. Messerschmitt sent in their modified Bf 110 design as the Me 210, and Arado responded with their all-new Ar 240.
The Me 210 was a straightforward cleanup of the 110, and used many of the same parts. The main differences were a modified nose area that was much shorter and located over the center of gravity, and an all-new wing designed for higher cruise speeds. On paper, the Me 210's performance was impressive. It could reach 620 km/h (390 mph) on two 1,350 PS (1,330 hp, 990 kW) Daimler-Benz DB 601F engines, making it about 80 km/h (50 mph) faster than the Bf 110, and nearly as fast as single-engine fighters of the era.
The Me 210's main landing gear followed some of the design philosophies that had resulted from the main change in the earlier Ju 88's main landing gear design, where each main gear had a single gear strut that twisted through 90º during retraction, to bring the main gear wheel resting atop the lower end of the main strut when retracted rearwards into the wing. Unlike the Ju 88, however, the Me 210's main gear wheels were "inside" the main gear struts when fully extended, while the Ju 88's were "outside" the struts.

Picture - Loading bombs onto an Me 210
The Bf 110 carried its ordnance externally, on the wings and fuselage, but this created drag; the Me 210 avoided this problem by housing the bombs in an enclosed bomb bay, in the nose of the aircraft. The Me 210 could carry up to two 500 kg (1,100 lb) bombs. The Me 210 had dive brakes fitted on the tops of the wings, and a Stuvi 5B bombsight in the nose, for shallow-angle dive bombing. In the fighter role, the bomb bay was fitted with four 20 mm cannons.
For defense, the Me 210's rear gunner was armed with two 13 mm (.51 in) MG 131 machine guns. These were fitted into half-teardrop-shaped turrets mounted on each side of the aircraft, and were remote-controlled from the gunner's position with a unique aiming setup, that had a rotating crossbar with a sideways-pivoting handgun-style grip and trigger at its center, "forked" at its forward pivoting end to fit around the crossbar. This unique aiming and control scheme rotated the crossbar axially, when the handgrip was elevated or depressed, to aim the guns vertically, and a sideways movement of the handgrip would pivot either one of the guns outwards from the fuselage for diagonal firing. The rear of the cockpit canopy's side glazing panels were bulged out to allow the gunner in almost any rearward-facing direction. The guns were electrically-fired, and an electrical contact breaker prevented the gunner from shooting off the Me 210's tailplane.

Picture - The rear defence barbettes of a Me 210 being maintained
An order for 1,000 Me 210s was placed even before the prototype had flown. In time, this would prove to be a mistake. The first prototype flew with DB 601B engines in September 1939, and was considered unsafe by test pilots. Stability was bad in turns, and it tended to "snake" even while flying level. At first the designers concentrated on the twin-rudder arrangement that had been taken from the 110, and replaced it with a new and much larger single vertical stabilizer. However, this had almost no effect, and the plane continued to oscillate. The Me 210 also suffered from terrible stalls. With the nose up or in a turn, the stalls whipped into spins when the automatic leading edge slats opened. The second prototype, Me 210 V2, was lost this way in September 1940, when the pilot could not get out of the resulting spin and had to jump. The chief test pilot commented that the Me 210 had "all the least desirable attributes an aeroplane could possess." It took 16 prototypes and 94 pre-production examples to try and resolve the many problems. Nevertheless, the RLM was desperate to replace the Bf 110s currently in service, and ordered full production in the spring of 1941. The type exhibited grossly inadequate handling characteristics, and a result, several elements of airframe were redesigned, including lengthening the fuselage, designated as lang ("long"). The Me 210C was built with DB 605 engines, as well as incorporating the changes to the airframe. The Hungarian authorities were satisfied with the Me 210C in its current state, and purchased a production license for the type, designated Me 210Ca (a = auslx¤ndisch) as well as for its DB 605 engines. Several airframes were also purchased, to be completed in Hungarian factories for practice while the assembly lines were set up. Production started in the Dunai Repx¼lÅ‘gépgyx¡r Rt. (Danubian Aircraft Plant) as the Me 210Ca with the DB 605B engine, under an agreement where the Luftwaffe got two of every three produced.
The Me 210 was eventually developed into the Messerschmitt Me 410, with DB 603 engines.
Operational history

Picture -
Deliveries to front-line units started in April 1942 and the plane proved to be even less popular with pilots. Production was stopped at the end of the month, by which time only 90 had been delivered. Another 320 partially-completed models were placed in storage. In its place the Bf 110 was put back into production. Although the Bf 110 was now equipped with the newer DB 605B engines and greater firepower, it was still an outdated design.
The Luftwaffe started receiving their Hungarian-built planes in April 1943, but the Hungarians didn't get their own until 1944; however, when they did enter service they were more than happy with them. Production ended in March 1944, when the factory switched over to produce the BF 109G. By that time, a total of 267 Me 210C had been built, 108 of them had been given to the Luftwaffe. They operated mostly in Tunisia and Sardinia, but were quickly replaced by the Me 410.
Variants
Me 210 A-0 Pre-production aircraft. Me 210 A-1 Single-seat twin-engined fighter-bomber, bomber destroyer. Me 210 A-2 Single-seat twin-engined dive bomber, bomber-destroyer aircraft. Me 210C Improved airframe, DB 605 engines. Me 210 Ca-1 Hungarian licensed production version of the Me 210C.
Operators
Germany
Luftwaffe operated 90 German-built Me 210A and 108 Hungarian-built Me 210 Ca-1.
Hungary
Royal Hungarian Air Force operated 179 Hungarian-built Me 210 Ca-1.
Japan
Imperial Japanese Army Air Service received one aircraft bought in Germany for tests and delivered aboard of U-Boat.
Airplane picture - Me 210 Diagram
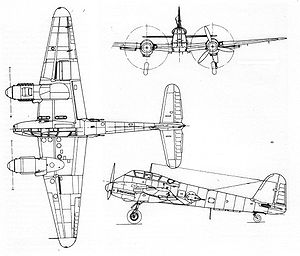
Specifications (Me 210 - long fuselage)
Data from Hornisse...The Last Zerstorer
General characteristics
Crew: 2 (pilot and gunner)
Length: 12.12 m (39 ft 9¼ in)
Wingspan: 16.34 m (53 ft 7â…› in)
Height: 4.28 m (14 ft 0½ in)
Empty weight: 7,070 kg (15,586 lb)
Max takeoff weight: 9,706 kg (21,397 lb)
Powerplant: 2x— Daimler-Benz DB 601F liquid-cooled inverted V12 engine, 1,350 PS (1,332 hp, 993 kW) each
Performance
Maximum speed: 564 km/h (304 knots, 350 mph) at 5,400 m (17,800 ft)
Range: 1,820 km (983 nmi, 1,130 mi)
Service ceiling: 8,900 m (29,200 ft)
Climb to 4,000 m (13,100 ft): 7.5 min
Armament
Guns:
2 x— 20 mm MG 151/20 cannons
2 x— 7.92 mm (0.312 in) MG 17 machine guns
2 x— 13 mm (0.512 in) MG 131 machine guns (rear armament)
Bombs: 2 x— 500 kg (1,100 lb) or 250 kg (550 lb) or 8x— 50 kg (110 lb) internal
Related development
Messerschmitt Me 310
Messerschmitt Me 410
Comparable aircraft
Focke-Wulf Fw 187
Messerschmitt Bf 110
"Hornisse...The Last Zerstorer". Air International, October 1981, Vol. 21 No. 4. ISSN 0306-5634. pp. 181-185, 197-200.
Living Warbirds: The best warbirds DVD series.
Source: WikiPedia